In today’s technology-driven world, having basic practical electronics knowledge is invaluable—even if you don’t come from an electronics background. Whether you’re a mechanical or civil engineer, a hobbyist, or someone interested in building DIY projects, understanding fundamental electronic components and how to use them can significantly enhance your problem-solving skills.
This blog serves as a comprehensive guide to practical electronics for beginners. You’ll learn about basic electronics concepts, commonly used components, and how to apply them in your projects. No complex jargon—just simple, easy-to-understand explanations.
🔥 Why Should Non-Electronics Professionals Learn (Practical) Electronics?
Understanding basic electronics allows you to:
- Enhance your project capabilities: Add electronics to mechanical or civil prototypes for automation or monitoring.
- Repair and troubleshoot: Identify and fix simple issues with electronic devices.
- Develop IoT projects: Control motors, sensors, and actuators using micro-controllers.
- Collaborate effectively: Communicate better with electronics engineers in multidisciplinary projects.
⚡ Basic Electronics Concepts
Before diving into components, it’s essential to understand some fundamental electronics concepts:
🟡 1. Voltage (V)
Voltage is the electrical potential difference between two points. It is measured in volts (V). Think of it as the “pressure” pushing the current through a circuit.
🔴 2. Current (I)
Current is the flow of electric charge through a conductor. It is measured in amperes (A). A higher current means more electrons are flowing.
🔵 3. Resistance (R)
Resistance opposes the flow of current. It is measured in ohms (Ω). Higher resistance reduces current flow, while lower resistance allows more current.
🟢 4. Power (P)
Power is the amount of energy used or dissipated in a circuit. It is calculated using: P=V×I
Where:
- P = Power in watts (W)
- V = Voltage in volts (V)
- I = Current in amperes (A)
🟣 5. Ohm’s Law
The fundamental law of electronics, Ohm’s Law, states: V=I×R
Where:
- V = Voltage
- I = Current
- R = Resistance
for better under stand of Ohm’s law, see the figure given below which represents the water and pipe analogy:
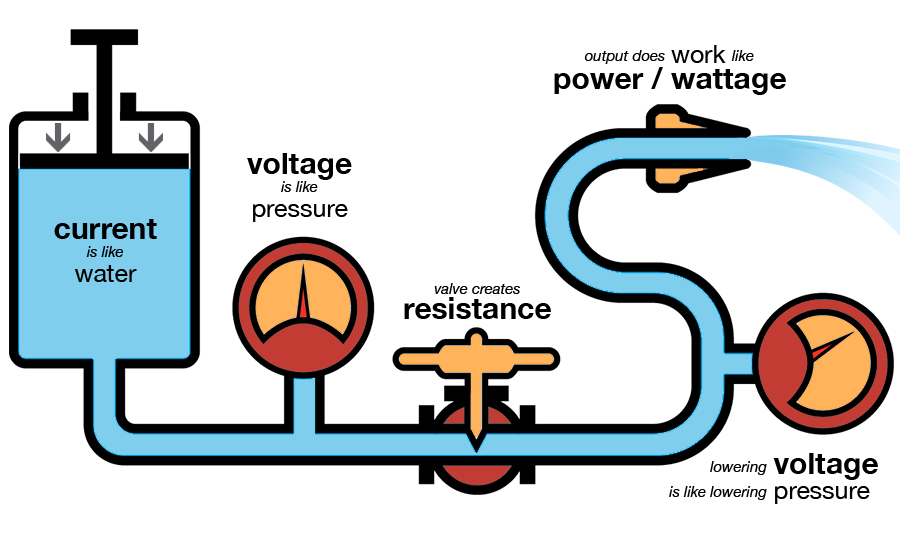
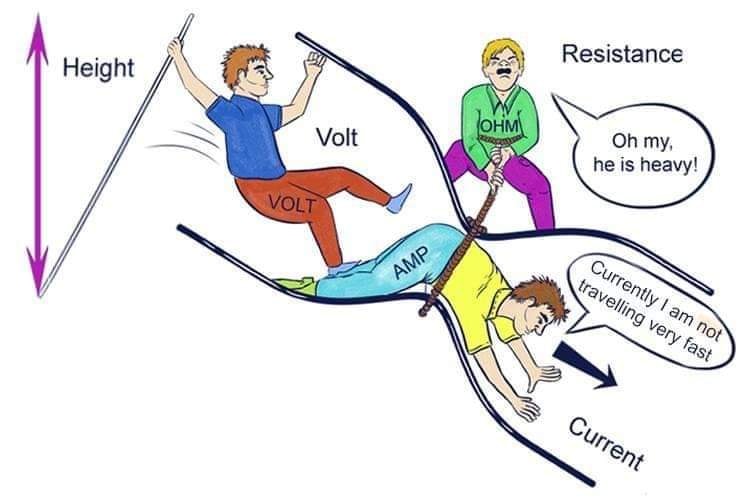
For further understanding of relation between, voltage, current and resistance, you can again refer the following figure:
✅ List of Basic Electronics and Mechanical Components Used in (Practical) Electronics
Let’s explore the most commonly used electronics components you’ll encounter in your projects.
⚡ 1. Basic Electronics Components
🔹 1.1 Passive Components in Practical Electronics
These components do not amplify or control the flow of electrical signals but influence them by resisting, storing, or dissipating energy.
✅ Resistors
- Fixed Resistors: Provide a constant resistance.
- Variable Resistors (Potentiometers): Adjustable resistance.
- Thermistors: Temperature-sensitive resistors.
- LDR (Light Dependent Resistor): Resistance varies with light intensity.

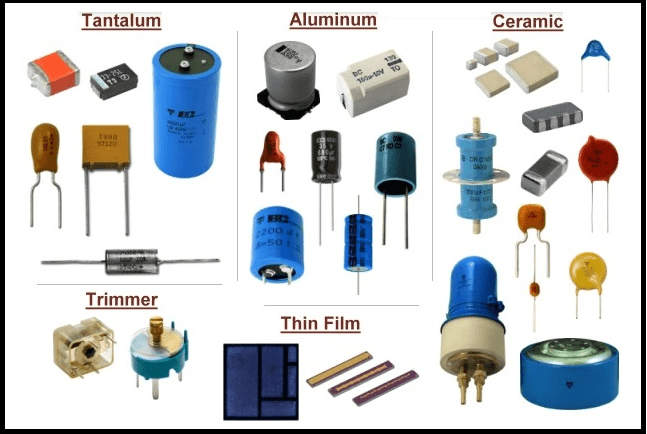
✅ Capacitors
- Ceramic Capacitors: Used for filtering and bypassing signals.
- Electrolytic Capacitors: Store large amounts of charge.
- Tantalum Capacitors: More stable and compact.
- Film Capacitors: Used in AC circuits.

✅ Inductors
- Store energy in a magnetic field when current passes through them.
- Used in filters, oscillators, and transformers.
🔹 1.2 Active Components in Practical Electronics
These components control the flow of current or amplify signals.
✅ Diodes
- Standard Diode: Allows current to flow in one direction.
- Zener Diode: Provides voltage regulation.
- Schottky Diode: Low voltage drop, used in high-speed switching.
- LED (Light Emitting Diode): Emits light when current passes through.

✅ Transistors
- Bipolar Junction Transistors (BJTs): Used for switching and amplification.
- MOSFETs: Efficient switching and power management.
- JFETs: Used in analog signal processing.

✅ ICs (Integrated Circuits)
- Op-Amps: For signal amplification.
- Timers (555 IC): Used in oscillators and timers.
- Microcontrollers (Arduino, ESP32, NodeMCU): Programmed to control electronic systems.
- Logic Gates ICs: Perform AND, OR, NOT, XOR, and other operations.
🔹 1.3 Power Components
Components that provide or regulate electrical power.
✅ Batteries
- Alkaline Batteries: Common for low-power devices.
- Lithium-ion (Li-ion) Batteries: Rechargeable, used in portable devices.
- Lead-acid Batteries: Used in heavy-duty applications.

✅ Voltage Regulators
- Linear Regulators (LM7805, LM317): Maintain constant voltage output.
- Switching Regulators: More efficient, used in SMPS circuits.

✅ Transformers
- Convert AC voltage from one level to another.
- Used in power supplies and signal isolation.

🔹 1.4 Input and Output Components
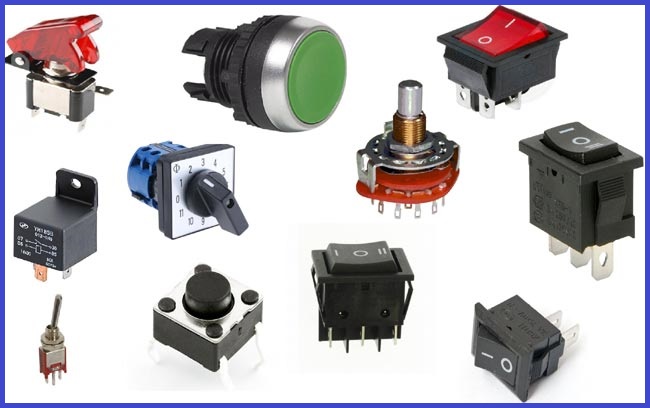
✅ Switches
- Push Button Switch: Momentary contact switch.
- Toggle Switch: ON/OFF switching.
- Rotary Switch: Select between multiple positions.
- Reed Switch: Magnetic field-activated switch.

✅ Connectors
- Jumper Wires: For breadboard connections.
- Headers and Sockets: For PCB mounting.
- Terminal Blocks: For wire-to-board connections.

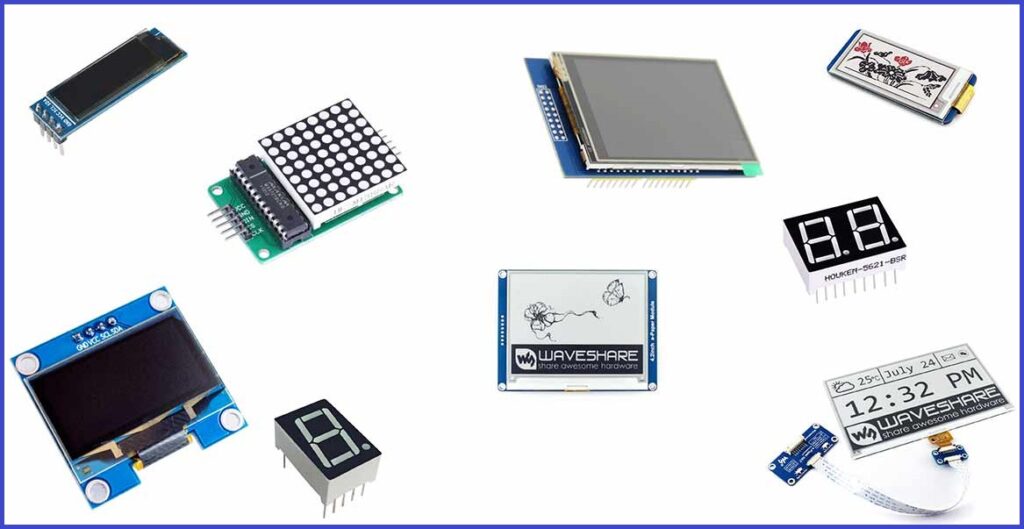
✅ Displays
- 7-segment Display: Shows numeric data.
- LCD Display: Shows alphanumeric characters.
- OLED Display: For high-contrast visual output.
- TFT Display: Full-color graphical display.

🔹 1.5 Sensors and Modules
✅ Sensors
- Temperature Sensors (LM35, DHT11): Measure temperature.
- Motion Sensors (PIR): Detect movement.
- Light Sensors (LDR, BH1750): Detect light intensity.
- Gas Sensors (MQ series): Detect gases like CO2, methane, etc.
- Distance Sensors (HC-SR04): Ultrasonic distance measurement.
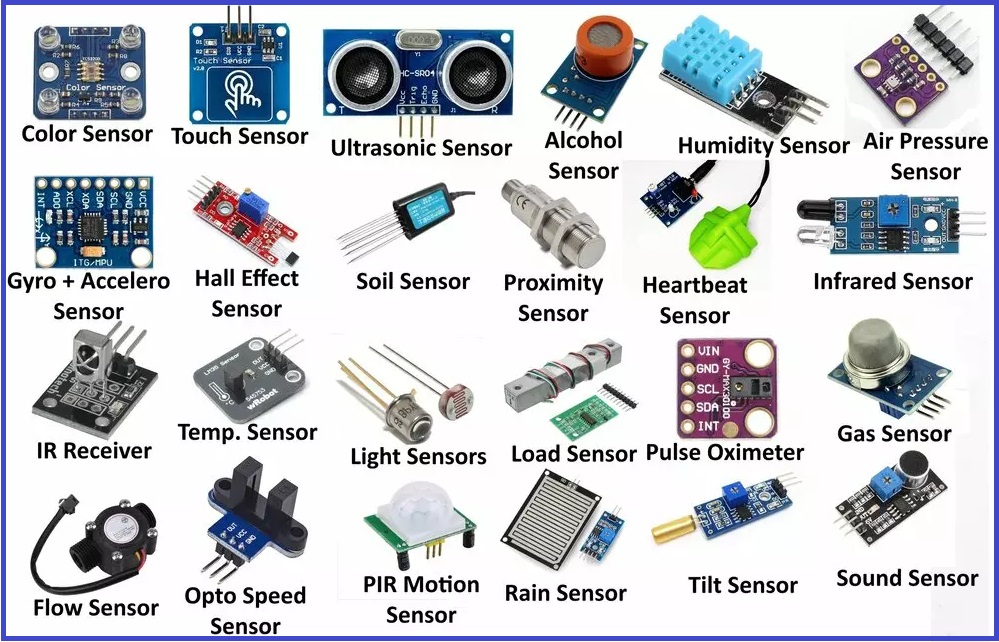

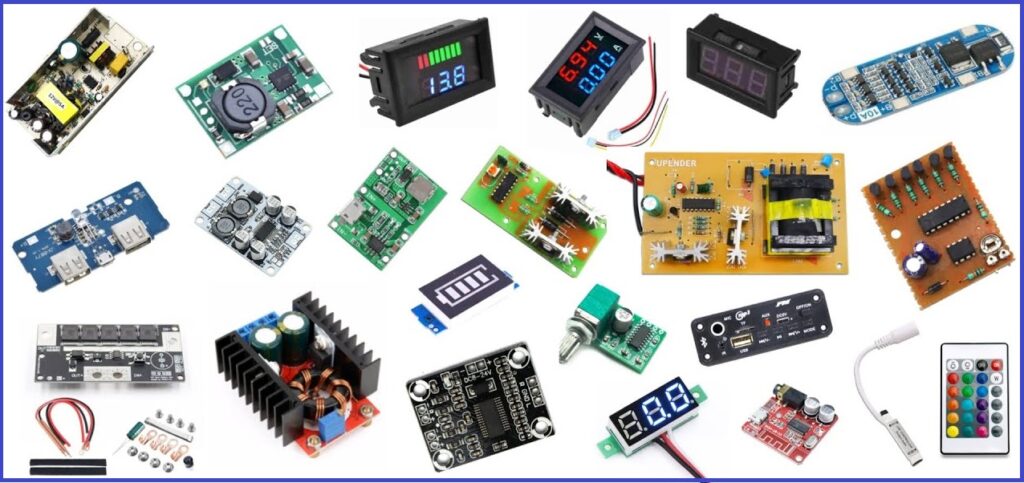
✅ Modules
- Wi-Fi Modules (ESP8266, ESP32): For IoT applications.
- Bluetooth Modules (HC-05, HC-06): For wireless communication.
- RFID Modules: For contactless identification.
- GPS Modules: For location tracking.

Also Read: HC-SR04 Arduino: How to use ultrasonic sensor with Arduino
🔧 2. Electro-Mechanical Components
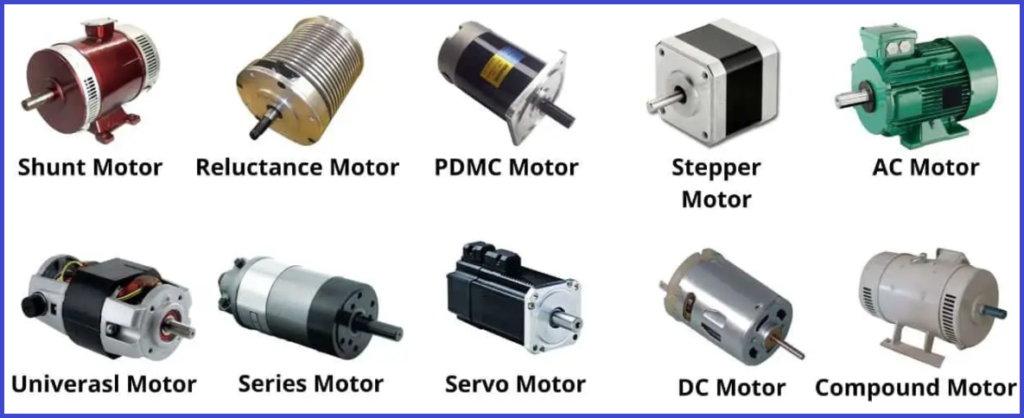
⚙️ Motors
- DC Motors → Basic motors used for continuous rotation.
- Stepper Motors → Rotate in steps, used for precise positioning.
- Servo Motors → Controlled rotation within a limited range.
- Brushless DC Motors (BLDC) → High efficiency, low noise.
- Geared Motors → DC motors with gearboxes for increased torque.

⚡ Actuators
- Solenoids → Convert electrical energy into linear motion.
- Linear Actuators → Move loads in a straight line.
- Servo Actuators → Precise control over angular or linear position.
- Pneumatic and Hydraulic Actuators → Fluid-powered motion.

🔊 Audio Components
- Buzzers → Generate sound.
- Speakers → Convert electrical signals to sound.
- Microphones → Convert sound to electrical signals.
- Piezoelectric Discs → Generate sound or vibration.
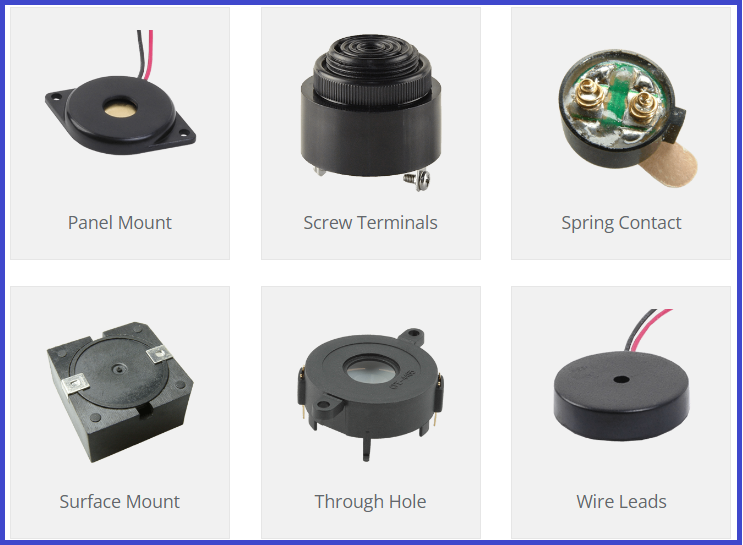

🔥 Electro-Mechanical Relays
- Electromechanical Relays → Use electromagnets to control switches.
- Solid-State Relays (SSR) → Use semiconductor technology for switching.
- Reed Relays → Magnetically operated switch.

🌡️ Thermal Components
- Heaters (Cartridge Heaters) → Generate heat for industrial applications.
- Fans and Blowers → Cooling systems for electronics.
- Thermoelectric Coolers (Peltier Modules) → Cooling by current flow.
🔋 3. Microcontrollers and Microprocessors
- Arduino (UNO, Mega, Nano) → Open-source microcontroller platform.
- Raspberry Pi → Single-board computer for complex applications.
- ESP8266/ESP32 → Wi-Fi-enabled microcontrollers for IoT projects.
- PIC Microcontrollers → Used in industrial and automotive applications.
- ATmega328P (Arduino UNO) → Popular microcontroller.

Here, I have given a short introduction of all the electronics and electro-mechanical components along with basic concepts in electronics.
In the Next section, we will learn about the first component that is –

Pingback: Tools for Practical Electronics: Essential Instruments and Accessories - TechKnowLab